Printed circuit boards or PCBs may look complicated, but that may not be the case. Simply put, PCBs are nonconductive materials with holes or pads designed on them. These holes help mount electrical components on them.
Along with mounting holes, they also have small embedded connections that you call traces. Traces act as wires, connecting the electrical components together and allowing them to function cohesively, which is critical for an electrical appliance’s functionality.
To understand the assembly process, you must know the basics of a printed circuit board.
PCB Basics
First, you should know that there are two ways to attach a component to a circuit board: the surface mount method, or SMD, and the Through Hole technique. In the surface mount technology, you have copper pads on the board, and you have to lay the components on top of them.
You then have a through-hole technique where you stick the ends of a component through the board and then solder them from the bottom. If you are new to PCBs and not skilled at soldering, the through-hole technique is the way to go. However, the components tend to be bigger, so you will not be able to create a compact design.
Below, we will discuss the step-by-step PCB assembly process on a large scale.
Soldering
The assembly process starts with soldering to the circuit board. The machine carries out an inspection at the start, in which it inspects the circuit board and ensures it is aligned. Once it is aligned, the machine will apply solder across the board’s surface evenly and smoothly. The machine ensures that the solder comes in contact with all the pads.
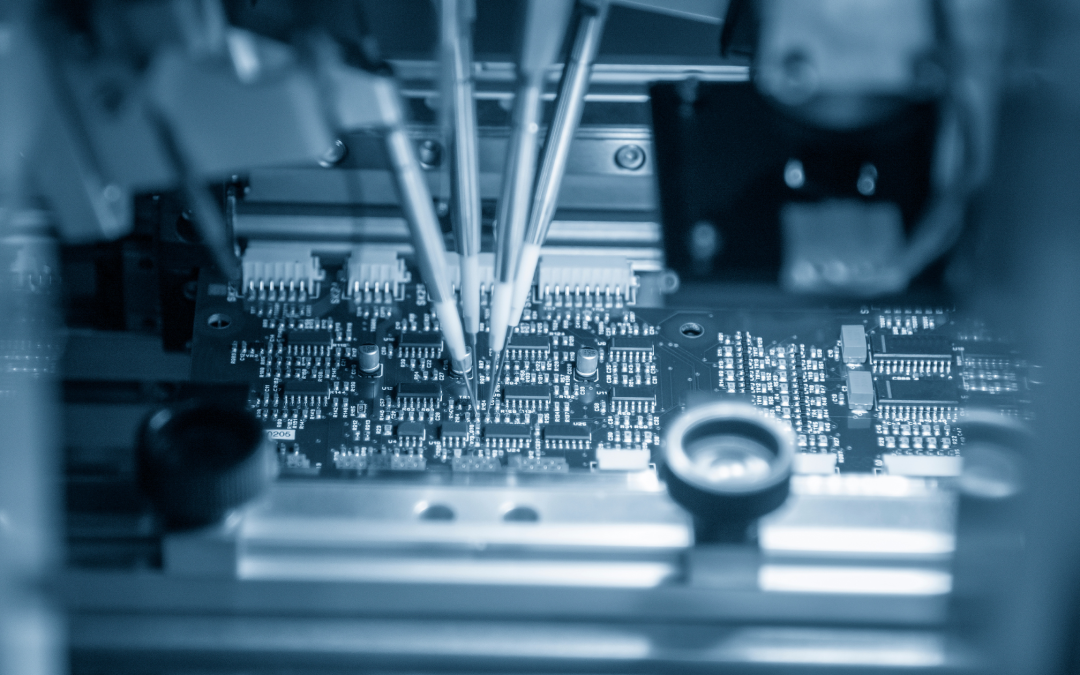
Pick and Place Machine
After soldering, the next assembly step requires the board to go to the pick-and-place machine. You must use a manual process for a low-volume prototype assembly, so you must place the board inside annually. The pick-and-place machine select’s it’s tools and then collects individual parts to place them on the board for rapid succession. After the pick and place process, the board is ready to refloat.
The head that moves back and forth on this machine can hold eight components simultaneously. The parts that come from reels include the tape and reel board. The head travels and picks up over eight parts at a time from the reels and advances them so that the next part is ready.
Refloat Process
Refloat process is crucial because the solder needs to melt for adherence. This will make the board good for both mechanical and electrical connections for all the parts. It travels across the big machine and comes out from the other side after being cooked. Once the solder cools, junctions between each part come into creation.
To Conclude
After the surface mount assembly, you can install through-hole components and create beta appliances. As you can see, manufacturing a printed circuit board involves a step-by-step process and careful considerations. The assembly process can, however, vary according to the size of the board and its electrical components.
As you can see, the PCB manufacturing process requires state of the art machinery and qualified expertise. If you want your printed circuit board assembly to be highly efficient and functional, you should look for a good manufacturer. Expert manufacturing companies are thorough with their design and assembly process, and can pave way for excellent appliances thanks to their sleek design.

Recent Comments